How to Install WordPress on Subdomain: 2 Proven Methods

A subdomain is a part of a domain name used for creating independent websites that serve as extensions of the main website. They typically house slightly different content that is still relevant to the primary domain.
For example, if you run an online store on your primary domain but want to add a blog, you can use a subdomain for it. It will be on a separate website but still connected to the main store site. An example of the subdomain would be blog.example.com.
If you want to install WordPress on subdomains and learn more about them, this article is for you. We will elaborate on two ways to create a subdomain, two methods to install WordPress on a subdomain, and what a subdomain can be used for.

1. Create a Subdomain
We will show you two ways to create a subdomain – through hPanel and the DNS zone editor.
hPanel is Hostinger’s easy-to-use proprietary control panel. It comes with all of Hostinger’s WordPress web hosting plans.
The DNS zone editor, on the other hand, is a feature most web hosting providers offer. It is used to create and manage DNS records.
Through hPanel
In order for this method to work, make sure your domain is pointing to Hostinger. It may take up to 24 hours after the creation of the subdomain for it to work properly.
Here are the steps to create a subdomain via Hostinger’s hPanel:
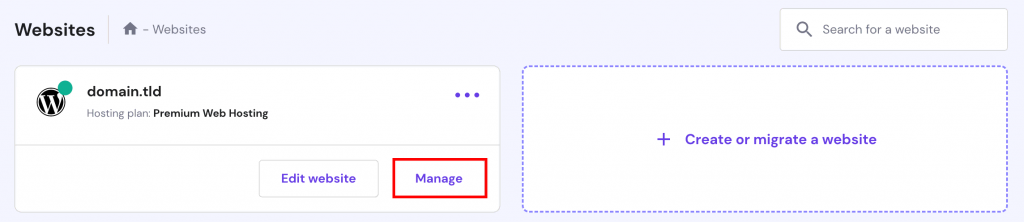
- Log in to hPanel and click on Websites on the navigation bar. Then select the Manage button near your domain.
- Once you’re on the Hosting Account page, go to Domains → Subdomains on the sidebar.
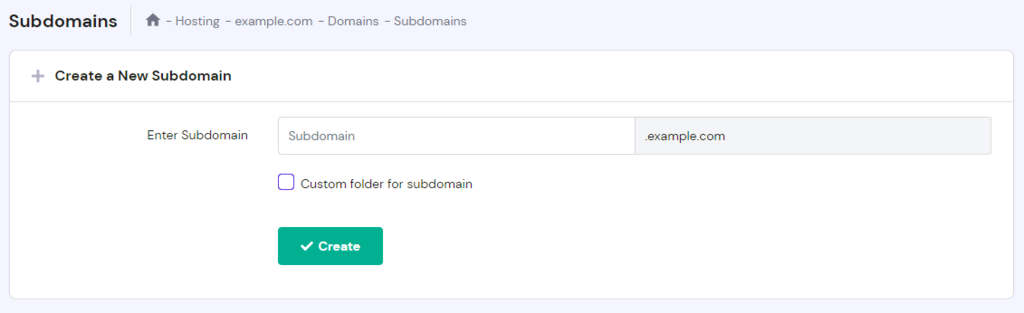
- On the Subdomains page, enter a new subdomain name in the Create a New Subdomain section. You can also specify a custom folder name for it by checking the Custom folder for subdomain box. Once finished, click Create.
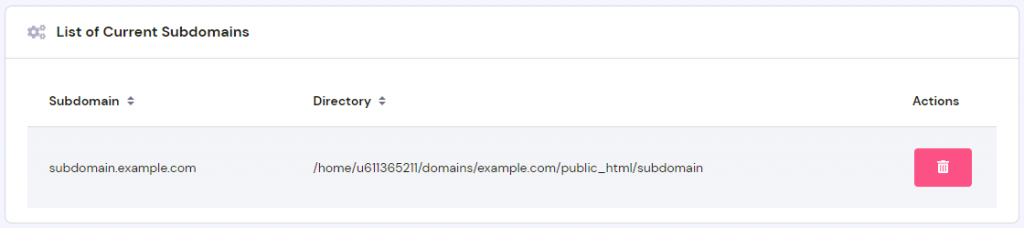
- Afterward, scroll down to find the subdomain you created on the List of Current Subdomains. On this page, you can also check the subdomain’s directory information and delete the subdomain.
Through the DNS Zone Editor
Another way to create subdomains is via the DNS zone editor located on your web hosting provider’s control panel. In this step-by-step guide, we will use hPanel.
Follow these steps to create a subdomain via hPanel’s DNS Zone Editor:
- Go to hPanel, navigate to Hosting, and click Manage next to your domain name.
- Once you’re on the Hosting Account page, find the Advanced section on the sidebar and click DNS Zone Editor.

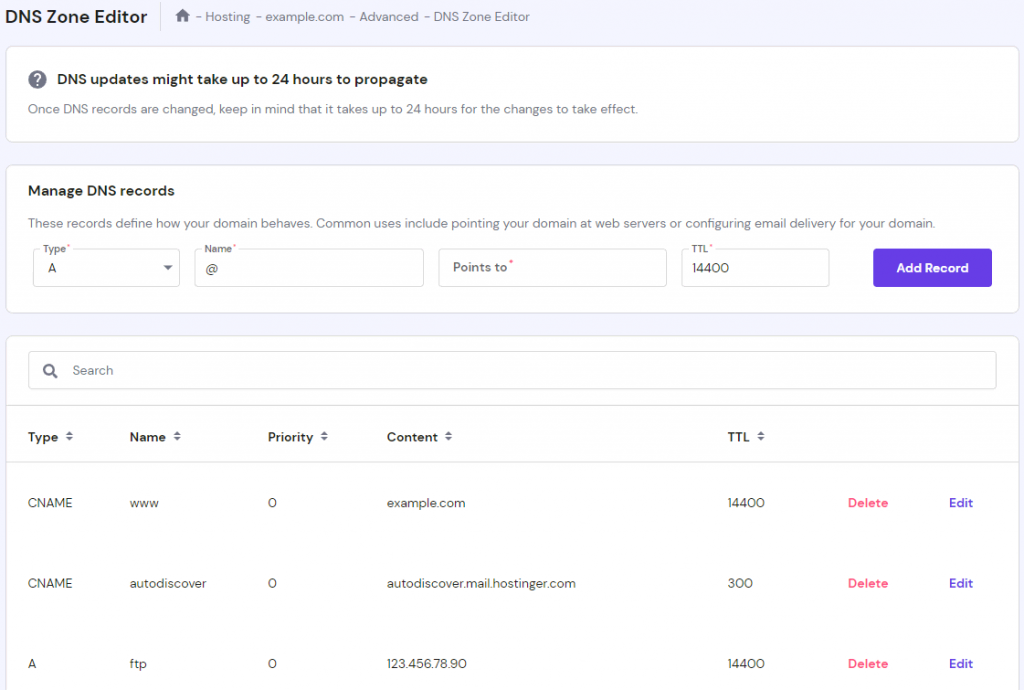
- On the DNS Zone Editor page, find the Manage DNS records section. Select A from the drop-down menu of DNS record types. Then, input a name, the IP address the subdomain points to, and the time to live (TTL). When finished, click the Add Record button.
- If you have successfully created the subdomain, the newly created DNS record will appear on the list of DNS records. Allow up to 24 hours for the change to take full effect.

2. Install WordPress on a Subdomain
Once you have created a subdomain, you can install WordPress on it.
There are two ways to do this – using the WordPress automatic installer or manually.
Through the Auto Installer
The auto installer helps people install various applications easily in a few clicks. We recommend beginners use this method to install WordPress to lower the chance of any errors.
Here are the steps to install WordPress on a subdomain using the one-click installer:
- Access your hPanel, go to the Hosting page, and click Manage beside your domain name.
- Scroll down to the Website section on the sider and click on Auto Installer.
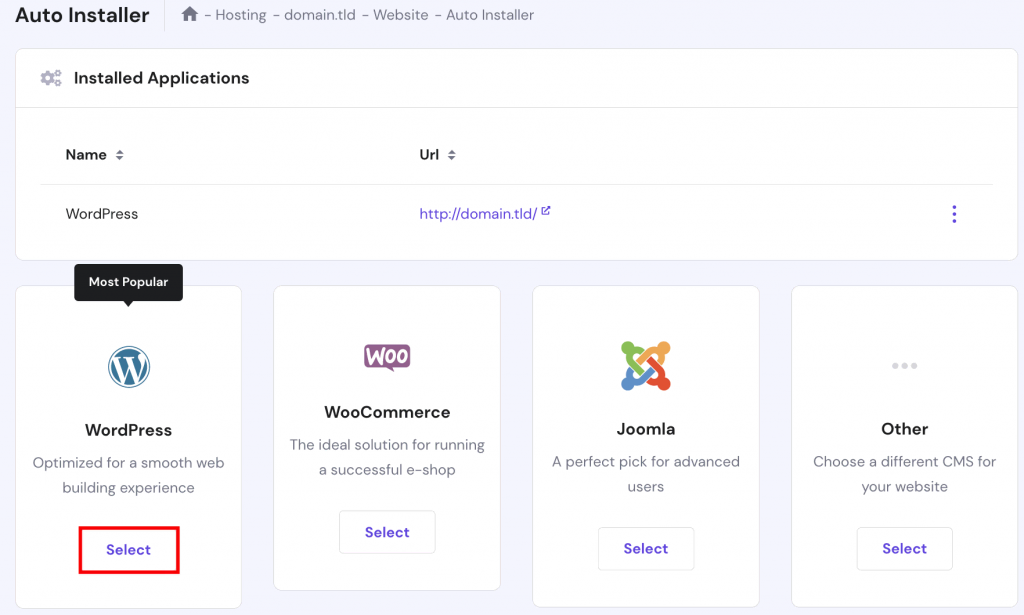
- On the new page, select WordPress.
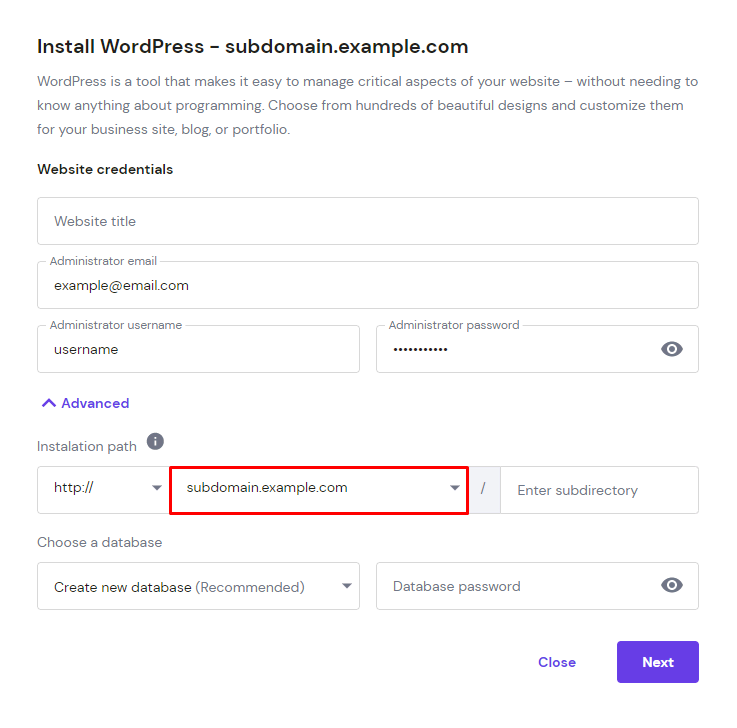
- The Install WordPress pop-up window will appear. Select the subdomain name from the drop-down menu and fill in all of the required information in the fields provided. Click Next and Install.
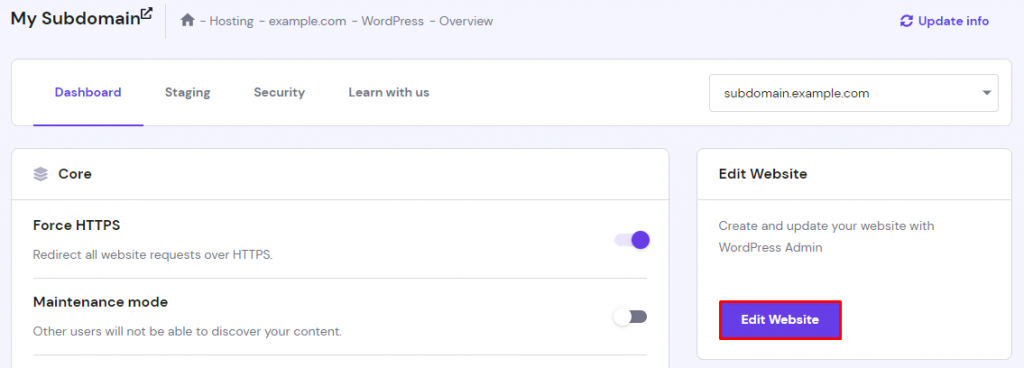
- Once the installation is complete, you will be redirected to the hosting dashboard for the subdomain you just created. Click the Edit Website button to access the WordPress admin dashboard and begin customization.
Installing WordPress on a Subdomain Manually
The manual method to install WordPress is a bit more complicated. However, it is useful if the automatic installer fails to work properly.
You can also install WordPress manually if you don’t want the built-in plugins provided by your hosting provider.
There are two ways to do this: by configuring an FTP client like FileZilla or using your hosting provider’s file manager. In this guide, we’ll use hPanel’s File Manager.
The following are steps to install WordPress on a subdomain manually:
- Head to the official WordPress website and download the WordPress package. Download the latest WordPress version and unzip the files afterward.
- You’ll have to upload the website files from your computer to the public_html/subdomain folder. To do this, log in to hPanel, navigate to Hosting, find your domain name, and click Manage.
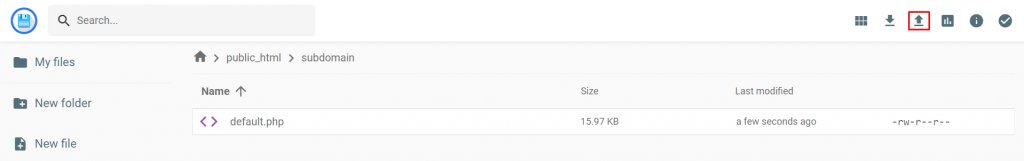
- On the Hosting Account page, scroll down to the Files section on the sidebar and click on File Manager.
- Click on the public_html root folder. Once you’re in the folder, find the subdomain folder and open it. Then, click the Upload Files icon on the navigation bar and upload the WordPress files you previously extracted.
- The next step is to create a new database and user so the web application can connect to it to retrieve information. To do this, return to the Hosting Account page on hPanel. Scroll down to the Databases section on the sidebar and click Management.
- In the Create a New MySQL Database and Database User section, fill out the database name, username, and password in the fields provided. Once finished, click the Create button. Don’t forget to note all the database credentials, including the alphanumeric strings. This information will be needed later.
- After creating the MySQL database and user, it is time to configure the wp-config.php file that tells WordPress about your database configuration. Return to the File Manager, click on the public_html folder, and open the subdomain folder.
- Find the wp-config-sample.php file and right-click on it. Select Rename, change the file name to wp-config.php, and click Rename when finished.
- Right-click on the wp-config.php file and select Edit.
- On the window that opens, look for DB_NAME, DB_USER, and DB_PASSWORD strings. Replace database_name_here, username_here, and password_here with the information you collected earlier, including the alphanumeric strings. Click the Save icon and close the file.
- To proceed with the manual WordPress installation, type the subdomain’s URL into your browser to access the WordPress setup page. Select a desired language from the menu and click the Continue button.
- Fill in the required website and admin information. Check the box next to Search engine visibility if you don’t want the site to be visible to search engines. Once finished, click Install WordPress to proceed with the installation process.
- Once the installation is finished, you will be notified that WordPress has been installed. Click Log In to access the admin dashboard and begin customizing your WordPress site.
What Is a Subdomain for?
Now that we have covered what a subdomain is, how to set it up, and how to install WordPress on one, we will elaborate on what people use subdomains for.
Expanding and Organizing Your Web Content
Subdomains are useful for creating websites separate from the main site while still using the same root domain. The separate WordPress site on the subdomain can have its own configuration and design.
Since the root domain remains the same, visitors will recognize that the subdomain website belongs to the same brand or company. This lets you maintain a consistent brand identity.
In addition, subdomains help you save money as you can make as many as you need without having to purchase and register multiple domains.
Dividing content across subdomains and specializing each subdomain for certain content or a specific target audience will also improve user experience.
For example, the blog.example.com subdomain can be used to separate blog posts from the main website’s content.
If you dabble in multiple areas of the creative industry, try using several subdomains to showcase different skills. You can use one subdomain to display your work as an artist, another to show off your photography skills, and a third to present your web design portfolio.
You can also set up subdomains to cater to specific groups of people – one subdomain dedicated to guests and another to registered users. In addition, subdomains can be used to target users from different regions.
Testing a New Site
Subdomains can serve as testing or staging grounds for new websites or new developments on an existing site.
On a subdomain, it’s possible to test out new features, themes, designs, layouts, plugins, or updates – all without affecting the actual live site.
Trying out new features or updates before committing to them is highly inadvisable, as the new elements can fail to appear how they’re supposed to. Errors can occur on the website as you’re testing the features, resulting in a site that’s inaccessible to users.
This can be especially harmful to mission-critical websites that must remain up at all times. Any downtime is detrimental to business websites, as it will lead to losses of traffic and potential customers.
Creating a Mobile Version of Your Site
For webmasters, making sure their websites can be viewed on all kinds of devices is a must. Many of them use subdomains for mobile versions of their sites. A subdomain used for this purpose will usually look something like m.example.com.
Mobile sites are especially important for SEO. For example, Google employs mobile-first indexing. This means it mainly uses the mobile version of websites for indexing and ranking.
As a result, websites without a mobile version or a responsive design will most likely suffer in terms of search engine ranking.
Starting an Online Business
If you have a website and want to build an eCommerce store on it, using a subdomain is an excellent way to do so.
The store will be on a separate website using the same root domain, letting people know that it is part of the main site. This way, you can launch an online store while leaving the main WordPress site untouched.
An example of this is the official In-N-Out Burger website. It houses an online store on the shop.in-n-out.com subdomain.
Another example is the official Porsche website. Its subdomain shop.porsche.com features Porsche merchandise, such as sunglasses and duffel bags.
If you have an online business idea, you can use a subdomain to set it up separately from your main site.
What To Consider Before Installing a Subdomain?
Despite the benefits of using a subdomain, using one may not be right for you, depending on your circumstances.
To help you decide if you should use a subdomain, we have listed some factors to consider before you install one:
- More work when building backlinks. Search engine crawlers regard subdomains as separate websites. This means you will need to put extra effort into collecting quality backlinks not only for the main domain but also for any subdomains if you want them to rank high on search engine results pages.
- Multiple admin dashboards. As all the subdomains have separate WordPress installations, users will have to navigate between different admin dashboards to manage their site, which can be time-consuming.
- Must add multiple website properties. You must add and verify each subdomain on Google Search Console. Settings customization and web performance tracking are also separate for each subdomain.
Subdomain vs. Subdirectory: Which One Is Better?
A subdomain is a child of the parent or main domain, sitting outside of the parent domain. On the other hand, a subdirectory or subfolder is a page that is a part of the main domain.
In a URL, the subdirectory will always follow the root domain. For example, /blog is a subdirectory of the root domain in the example.com/blog URL.
Whether to use subdirectories or subdomains depends on your needs as well as the platform you are using.
If the content you want to feature is closely related to the main subject of the root domain, it’s a good idea to use the subdirectory system. On the other hand, if the content differs greatly from the main focus of the root domain, we recommend using a subdomain.
That said, you’ll have to set up multiple subdirectories to leverage the WordPress multisite feature.
Let’s take a look at the official website of the New York Giants, a professional American football team. It uses subdirectories for content such as team news, videos, photos, schedule, roster, and podcasts.
Here is what the giants.com/video/ subdirectory looks like:
For its merchandise shop, however, the site uses the shop.giants.com subdomain:
Subdomains and SEO
SEO experts debate the effects of subdomains on SEO.
According to John Mueller, a Webmaster Trends Analyst at Google Search Central, using subdomains is fine for ranking on Google.
As we mentioned earlier, however, each subdomain has to be submitted to the Google Search Console separately. As subdomains are treated as separate websites, it may take a few days for the content to be crawled and properly indexed before ranking.
That said, using subdirectories for closely linked content is preferable and may lead to increased traffic.
Conclusion
A subdomain is an independent website that sits outside of the root domain but is still connected to it. Blog.example.com is an example of what a subdomain looks like.
We have discussed two methods of installing WordPress on a subdomain – using the WordPress Auto Installer or manually.
For beginners, we recommend installing WordPress with the automatic installer. Although the manual WordPress installation is more complex, it is useful when the automatic installer fails or when you want to install WordPress without the plugins included with your web hosting.
Subdomains can be used for various purposes, such as expanding and organizing web content, testing new websites, creating a mobile version of the site, and starting an online business.
Before you install a subdomain, remember that you’ll have to put extra effort into building backlinks, managing separate WordPress admin dashboards, and adding multiple websites to the Google Search Console.
We hope this guide has helped you install WordPress on subdomains. If you have any comments or questions, let us know in the section below.
Learn More About WordPress
What is WordPress
How to Login to WordPress
How to Create a Multilingual WordPress Site
How to Duplicate Pages and Posts on WordPress
How to Delete WordPress
How to Use WordPress Importer
How to Export WordPress Users
WordPress Taxonomy Guide
Guide to WordPress Revisions
Install WordPress on Subdomain FAQ
Here are some common questions and answers about the topic.
How Do I Link My WordPress Page to a Subdomain?
The steps to link a WordPress page to a subdomain depend on your hosting provider. First, create a subdomain in the DNS settings of your hosting account. Once you have the subdomain, head to your WordPress dashboard to install the WP Subdomains plugin to use the wildcard redirects feature.
Can I Redirect a URL to a Subdomain?
Yes, and doing so can help visitors find the correct page on the web. Redirection of URLs can be done in several different ways, depending on what type of website you have and the resources available to you. The most common methods include server-side redirection.